What is brand architecture?
Brand architecture is the hierarchal structure of a company’s externally-facing products and services and their relationship to the parent company. It’s an organizational tool that provides logic and definition, helping audiences understand a company’s offering.
As companies grow, introduce new products or services, or acquire businesses, their brand portfolios become more complex — and so do their brand architectures. The lines between offerings can become less differentiated and their respective roles less clear.
“The goal should be to have the fewest relevant brands needed to meet the business goals1,” says David Aaker, Vice-Chairman of brand consulting firm Prophet and author of Brand Portfolio Strategy: Creating Relevance, Differentiation, Energy, Leverage, and Clarity.
Why does this matter?
Without a strategy for companies to manage brand architecture, customers can get confused. If the benefit, role, or relevance are unclear, customers won’t consider the offer. An undefined brand architecture makes it hard for customers to find what they are looking for.
Companies that actively manage their brand architecture are more relevant to customers, build and protect brand equity, and facilitate business growth.
The five brand architecture models
Brand architecture decisions should be driven by a company’s business strategy, vision, and market needs. Companies usually adopt one of the following models:
Branded house, Sub-brand, Endorsed, House of brands, or Hybrid.
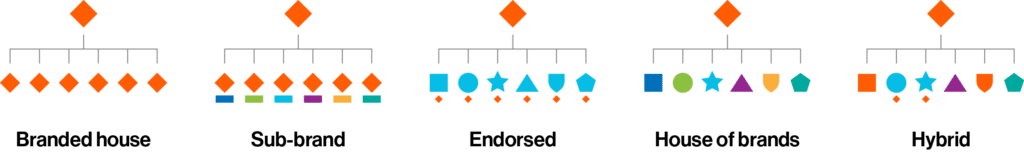
The models can have significant competitive advantages. A 2016 study published in Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science found that sub-brand and branded house architectures deliver superior stock returns, and house of brands architecture is associated with lower firm-specific risk.2
Download our Brand Architecture Model Decision Tool
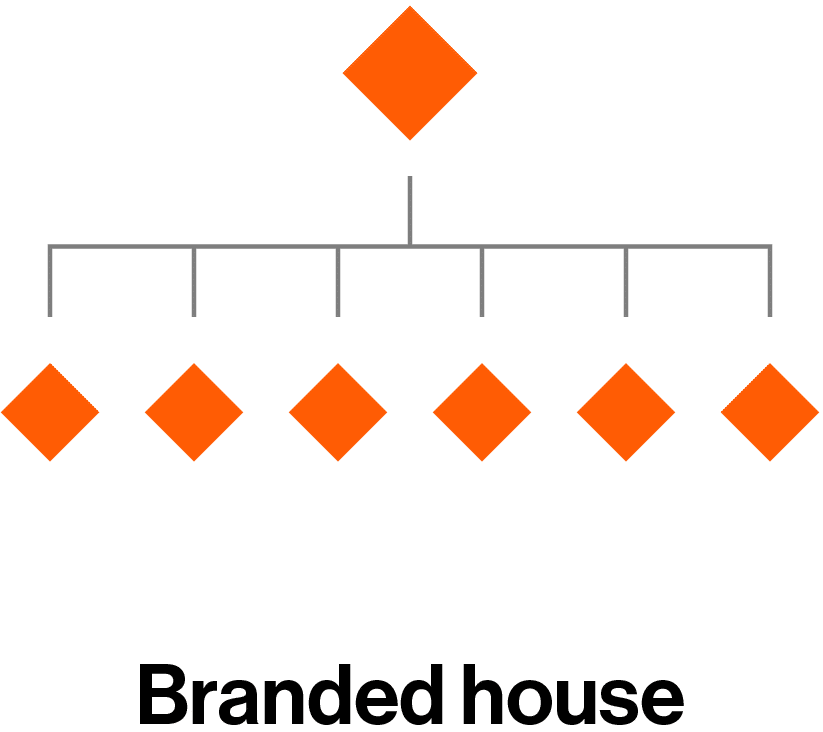
Branded house architecture
In a branded house, the company itself is the brand, and all its products and services share one name and visual identity. Specific offerings might include a functional descriptor but are clearly defined as part of the parent brand.
Branded house architecture is recommended if a brand is being launched for the first time.
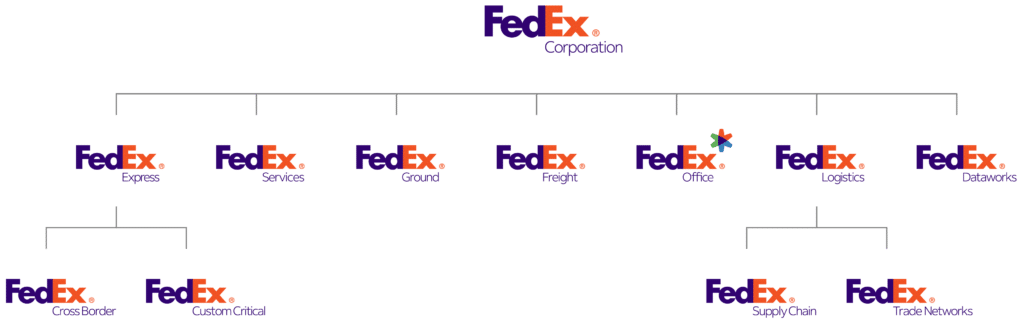
Branded house example: FedEx
Each service is represented by the FedEx parent logo and appended with a functional descriptor. Although offerings are differentiated, the brand is clearly perceived as FedEx.
Branded house strengths and weaknesses
STRENGTHS
- A branded house requires the least amount of financial investment and time because companies support one brand rather than many.
- A branded house enjoys cohesiveness and clarity while reducing confusion.
- A branded house builds awareness and customer loyalty by emphasizing a central brand promise instead of specific product features.
Weaknesses
- A branded house architecture makes it harder to expand into new markets or product categories unrelated to the core business.
- A bad experience with one part of the company can affect the entire organization. If one product or service fails, all of them can be negatively impacted.
- There’s less flexibility to market products or services independently or develop product-specific value propositions.
Sub-brand architecture
Sub-brands append the master brand with a unique product or service name. They target a new market while maintaining a strong association with the master brand. Sub-brand names should be differentiating and ownable, not generic, so they aren’t co-opted by competitors.
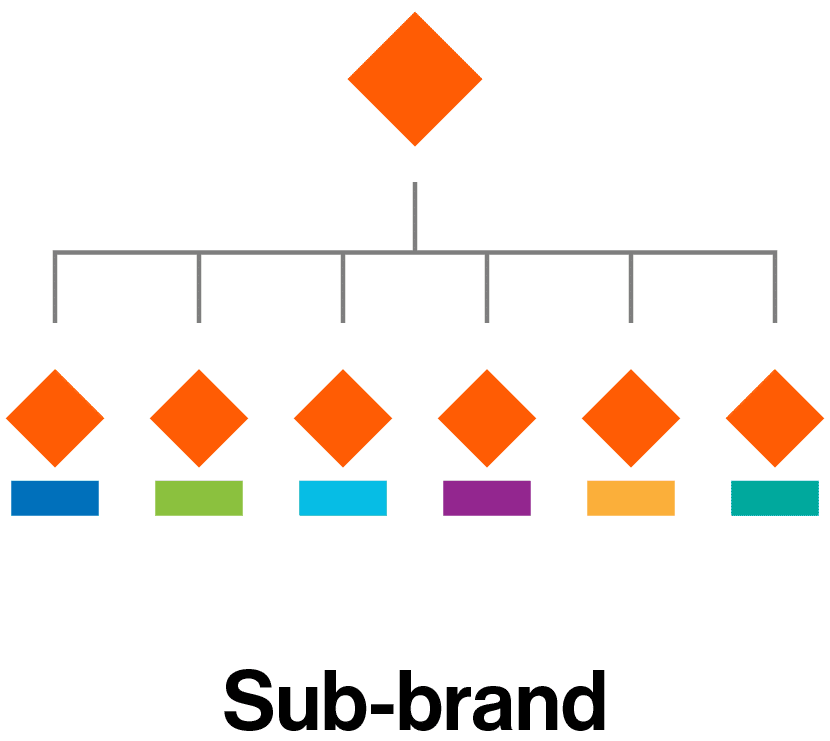
Sub-brand example: Toyota
The Toyota portfolio includes the Prius, Corolla, and Tacoma sub-brands. Each has close ties to the Toyota brand but markets to different categories and audiences.

Sub-brand architecture strengths and weaknesses
STRENGTHS
- Sub-brands provide flexibility for the parent brand to access niche markets or categories.
- Sub-brands can establish expectations, benefits, messaging, and personalities that are differentiated from the parent brand.
- Customers are more likely to try a brand’s other products or services if they trust the sub-brand.
Weaknesses
- Marketing separate sub-brands is costly and requires more investment and resources.
- Extending into markets or categories that aren’t a natural fit can tarnish the master brand.
- Positioning a brand across too many product or service categories can dilute brand equity and lessen its impact.
Endorsed brand architecture
With endorsed brands, products or services have unique brand identities but leverage the parent brand’s equity through a discreet endorsement.

Endorsed brand architecture example: 3M
Scotchgard, Post-it, and Command are unique brands that apply an endorsement to maintain their association with the 3M parent brand.

Endorsed brand architecture strengths and weaknesses
STRENGTHS
- Endorsed brands have more independence and can create their own identity and brand positioning.
- Endorsed brands can leverage the familiarity of the parent brand to establish credibility and trust.
- Product and service brands can compete in new markets without alienating the parent brand’s existing customers.
Weaknesses
- Each brand within the portfolio requires its own strategy, assets, and resources.
- Budgets will be spread thinly across multiple endorsed brands rather than the parent brand alone.
- A problem with an endorsed brand could negatively impact the larger brand portfolio.
House of brands architecture
A house of brands consists of several independent brands with no perceived connection to the parent brand. Often, the parent brand is known only to the investment community rather than to consumers.

House of brands example: Unilever
Unilever has a house of brands architecture with over 400 independent brands. Dove, Axe, Hellman’s, Suave, Ben & Jerry’s, and Q-tips are all part of its portfolio, but the Unilever parent brand is practically invisible to consumers.

House of brands architecture strengths and weaknesses
STRENGTHS
- Brands have the freedom to target distinct market segments with specialized value propositions, such as product features and price points.
- In times of crisis, the negative impact on one portfolio brand is isolated from other portfolio brands and the parent company.
- The parent company can expand into new markets without risking credibility or alienating existing customers.
Weaknesses
- Building brand awareness takes significant investment and time.
- Positive associations of one brand won’t transfer to other brands — each brand needs to build its reputation individually.
- There are operational and legal complexities associated with owning multiple entities.
Hybrid brand architecture
Many companies require a custom-tailored solution to meet specific business needs. It’s common to combine aspects of two or more models to form a hybrid. A “pure” branded house, sub-brand, endorsed, or house of brands model is somewhat rare.
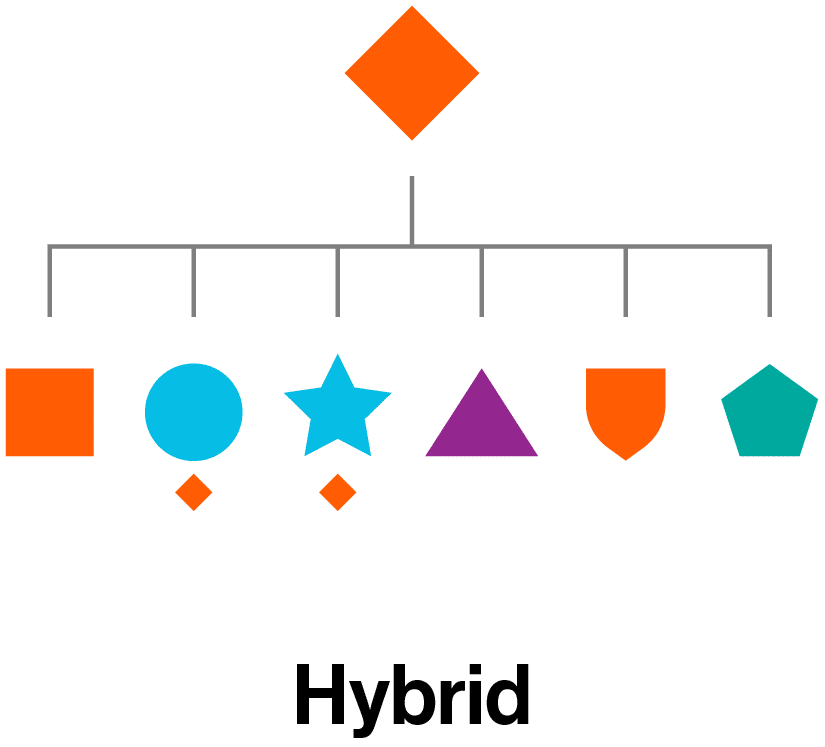
Hybrid brand architecture example: Amazon
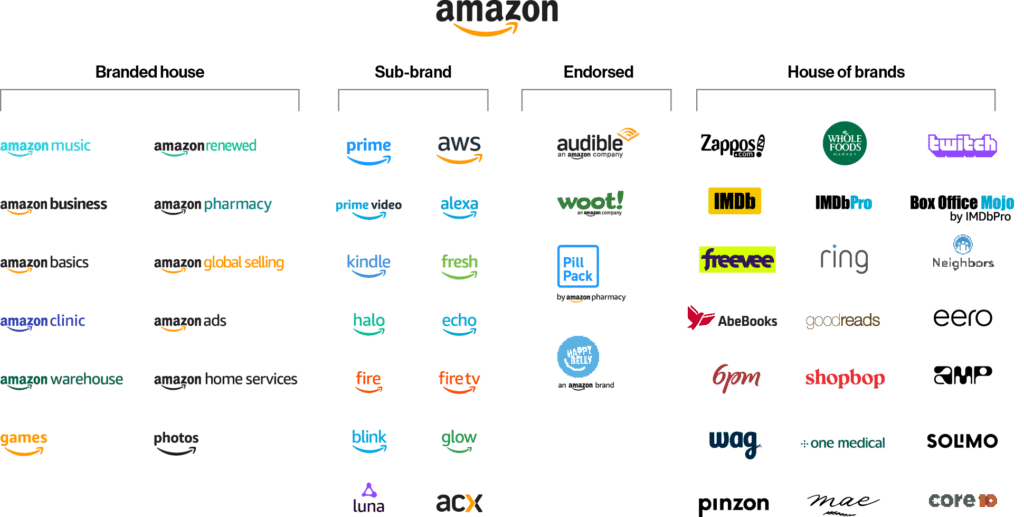
Amazon combines aspects of several models to form a hybrid brand. Some products and services align with the master brand, while others remain independent or somewhere between.
Hybrid brand architecture strengths and weaknesses
STRENGTHS
- Companies have the flexibility to leverage the equity of the master brand or create entirely new brands when needed.
- Brands can target distinct market segments with specialized value propositions, such as product features and price points.
- Mergers and acquisitions are easier to integrate into the model.
WeaknesseS
- The organization can appear disorganized and cause customer confusion.
- It’s costly to market and promote separate brands.
- Complexity will require more time and resources to manage. Each brand will need its own strategy, assets, and promotion.
Need help deciding on a Brand Architecture Model? Download our Decision Tool.
Considerations for choosing a brand architecture model
How do you choose an effective model for your brand architecture? Consider the five models as a starting point, not the end goal, and adapt them to suit your unique business needs. Ask questions to identify factors that influence decisions:
- What is your long-term vision for the company?
- Do your products and services cater to similar customer segments with similar values?
- Will it be easy to tell one cohesive story that makes sense to audiences?
- Would consolidation compromise a brand’s market share or leadership position?
- Would changing the brand alienate existing customers? Will they accept or resist the change?
- Can your company support the financial investment and resources required to support multiple brands?
Clarify brand architecture to improve your bottom line
A well-implemented brand architecture can differentiate your offering, clarify relevance, and demonstrate how products and services are positioned to address specific customer needs. With a thoughtful approach, brand architecture can strengthen your brand portfolio, help drive growth, and increase your company’s bottom line.
Notes
- Aaker, D. A., Brand Portfolio Strategy: Creating Relevance, Differentiation, Energy, Leverage, and Clarity, New York: Free Press, p. 16 (2004).
- Hsu, L., Fournier, S., and Srinivasan, S., “Brand architecture strategy and firm value: how leveraging, separating, and distancing the corporate brand affects risk and returns,” Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 44: 261–280 (2016).