FRAMEWORK
How to Implement NIST Compliant Generative AI Governance
- Pariveda’s Generative AI Risk Management Maturity Model offers a structured approach to assessing the current state of affairs and understanding how to enhance and close the gap towards a desired maturity level.
Generative AI (gen AI) is transforming industries with its ability to create content, automate processes, and enhance decision-making. However, this power comes with significant risks, such as privacy violations, bias reinforcement, security breaches, and legal concerns.
Proper governance and risk management, aligned with established frameworks like the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) AI Risk Management Framework (RMF), are essential to mitigate these risks and ensure safe and responsible AI deployment. NIST provides customers with enhanced security, better compliance, improved risk management, and, often, a stronger reputation in the industry.
So, how do you establish a gen AI governance strategy based on NIST guidelines? Pariveda’s Generative AI Risk Management Maturity Model offers a structured approach to assessing the current state of affairs and understanding how to enhance and close the gap towards a desired maturity level. This will allow you to systematically improve your risk management processes.
NIST AI Risk Management Framework gen AI profile (a.k.a NIST.AI.600-1)1
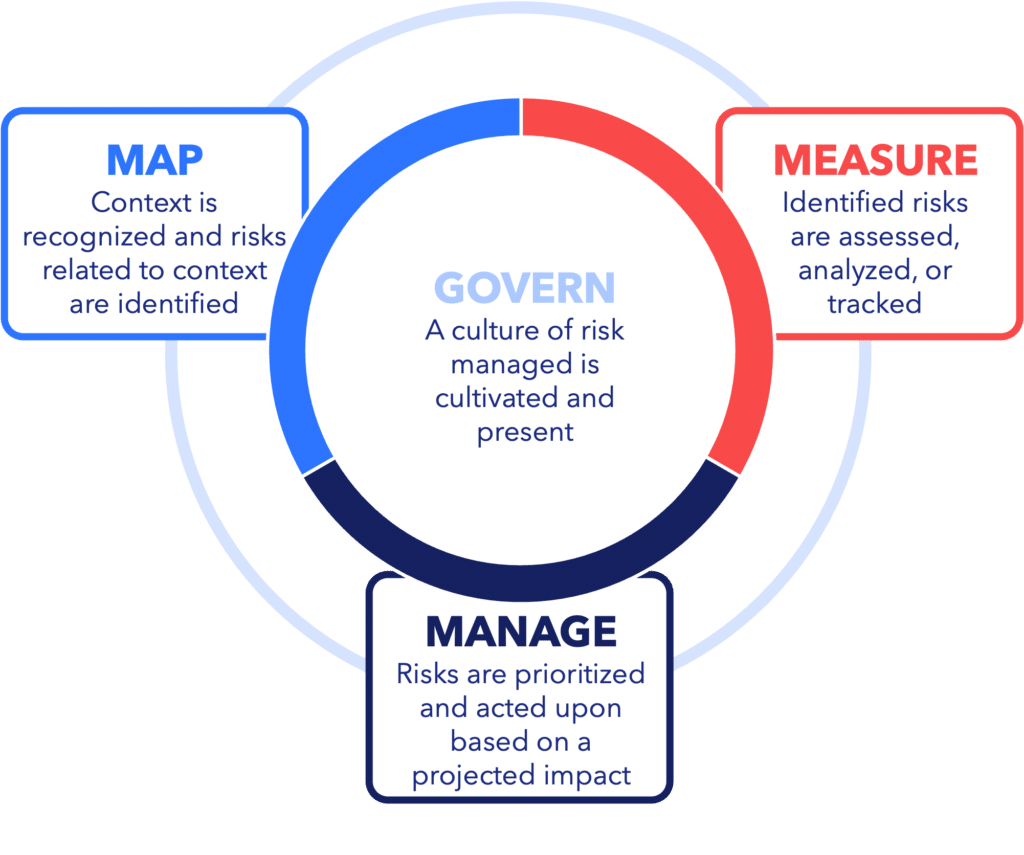
NIST AI RMF encourages organizations to adopt governance frameworks that prioritize risk management, accountability, and transparency for AI systems. The gen AI Profile uses four categories to govern, map, measure, and manage risks associated with activities or business processes. It further defines risks that are novel to or exacerbated by the use of generative AI and provides a set of suggested actions to help organizations deal with risks.
CATEGORY 1
Establish a governance framework
Govern is a cross-cutting function that is infused throughout gen AI risk (GAI) management and informs the other three functions.
- Policy and strategy development: Organizations are encouraged to define and document policies and strategies that align with their goals and risk tolerance concerning GAI. These strategies should address GAI’s impact on privacy, fairness, accountability, and transparency.
- Roles and responsibilities: Create clear accountability structures by appointing dedicated GAI governance teams. This includes designating leadership for GAI risk management and ensuring that all relevant stakeholders are involved.
- Risk management practices: Organizations should implement practices for continuously identifying, assessing, managing, and monitoring GAI risks. This involves regular reviews and updates of GAI risk management practices to stay aligned with evolving technologies and regulations.
- Documentation and reporting: Maintaining detailed documentation of GAI systems, their risks, and the steps taken to mitigate those risks is crucial. Regular reporting ensures transparency and helps evaluate the effectiveness of the GAI risk management processes.
- Stakeholder engagement: Engage with internal and external stakeholders, including legal, ethical, and technical experts, to inform risk management strategies and practices.
CATEGORY 2
Map the AI system and identify risks
The Map function establishes the context to frame risks related to GAI systems that are critical to risk management.
- Identification of risks: Organizations are required to identify and document risks, including potential impacts on privacy, security, and fairness. This involves understanding the scope and context in which GAI systems operate.
- Assessment of risk factors: Once risks are identified, organizations should assess the severity and likelihood of these risks materializing. This step includes evaluating both direct and indirect consequences of GAI deployment.
- Mapping GAI systems: Organizations should create comprehensive maps of GAI systems, detailing how data flows through these systems and identifying points where risks may be introduced. This also involves mapping out the decision-making processes within GAI systems to ensure transparency and accountability.
- Alignment with organizational goals: The actions within Map ensure that GAI systems and their associated risks are aligned with an organization’s overall risk management strategies and objectives. This alignment helps prioritize actions that mitigate the most significant risks first.
CATEGORY 3
Measure risk and performance
The Measure function uses quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method tools, techniques, and methodologies to analyze, assess, benchmark, and monitor GAI risk and related impacts over time.
- Define measurement objectives: Establish clear objectives for what needs to be measured in terms of GAI risks and their impacts.
- Develop and implement metrics: Create and apply metrics that are aligned with the defined objectives. These metrics should measure various aspects of GAI risk, including technical performance, fairness, and security.
- Data collection: Systematically gather data that is relevant to the metrics and necessary for evaluating the performance and impact of GAI systems.
- Evaluate metrics: Regularly assess the effectiveness of the metrics and update them as needed to ensure they remain relevant and accurate.
- Communicate findings: Share measurement outcomes with stakeholders in a clear and understandable manner to inform decision-making and risk management strategies.
CATEGORY 4
Operationalize and monitor AI risk
The Manage function allocates risk management resources to mapped and measured risks on a regular basis as part of an ongoing governance process.
- Risk management: Implement comprehensive risk management processes that continuously monitor and address GAI risks. This includes adapting existing organizational risk management strategies to account for GAI-specific risks.
- GAI system management: Institute the proper operation, security, and privacy of GAI systems throughout their lifecycle. This includes managing the deployment, scaling, and maintenance of GAI systems while ensuring compliance with relevant laws and standards.
- Accountability and transparency: Establish clear lines of accountability for GAI system outcomes and make the GAI system’s operations transparent to stakeholders. This involves documenting decisions, actions, and their impacts.
- Stakeholder engagement: Actively involve stakeholders (e.g., users, affected communities) in the management process to ensure their concerns and feedback are incorporated into GAI system governance.
Pariveda’s Generative AI Risk Management Maturity Model
Now that you understand the NIST gen AI Profile categories, you will need a structured approach to assess your as-is state and define a desired target for governance and risk. That is why we created Pariveda’s Generative AI Risk Management Maturity Model in accordance with NIST categories.
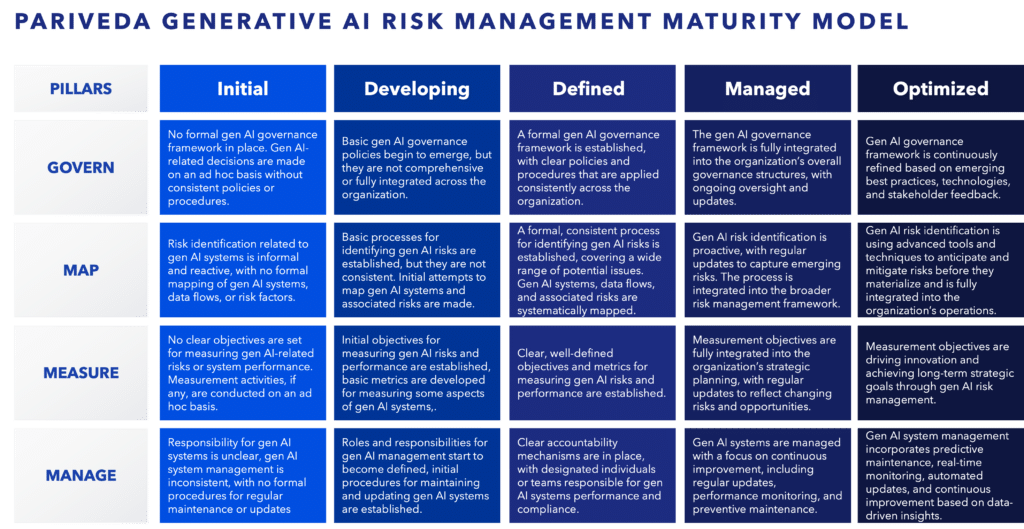
This tool will help you and your teams assess your current gen AI maturity and envision your desired future state for gen AI adoption and use. Our maturity model is meant to help you improve and evolve your capabilities and align with best practices. For tailored guidance and expert support, we are ready to partner with you to achieve your organization’s success.
Conclusion
Governance is not a one-time effort—it is an ongoing process that requires adaptability, transparency, and continuous improvement. Following the NIST framework provides a strong foundation for managing the complexities and risks of gen AI while driving innovation and business success.
Implementing a robust gen AI governance framework is the first step to mitigating risks associated with gen AI while maximizing the tremendous benefits it offers an organization. By establishing clear policies, identifying and measuring risks, and ensuring ongoing monitoring and accountability, organizations build trust in AI systems with their stakeholders and effectively navigate the complex regulatory landscape.