Navigating cloud costs
Cloud computing has been shown to significantly lower IT costs while providing powerful computing and storage resources. However, its ability to be agile and scalable can lead to runaway costs that can be difficult to pinpoint. Creating and maintaining a comprehensive cloud strategy is vital to long-term success. Cloud cost containment all starts with awareness and integrated planning. As such, we have crafted this article to bring visibility to 5 of the most common hidden cloud costs – improperly sized infrastructures, misplaced regions, idle workloads, multi-cloud data egress fees, and not utilizing reserved instances. This article will help you illuminate these hidden costs and give you ideas to start eliminating extra cost centers.
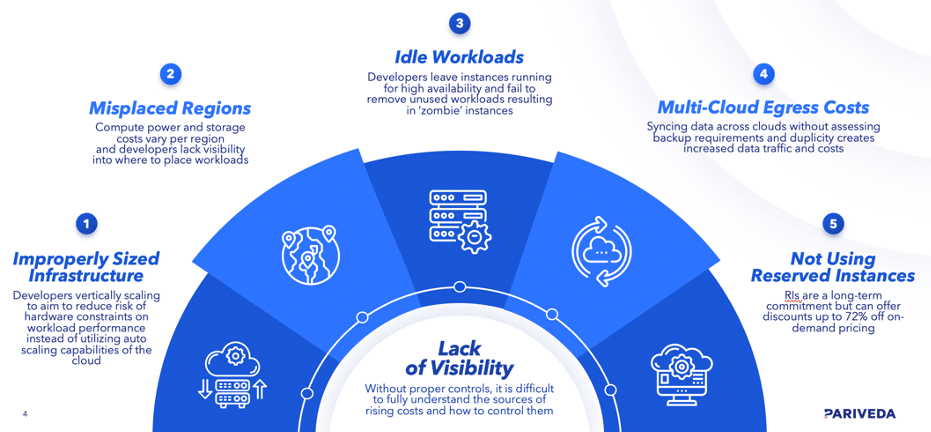
Improperly sized infrastructure
Properly sized infrastructure is a critical component of being successful in the cloud. Sometimes referred to as rightsizing, the process of matching your cloud resource sizes with performance and capacity allows organizations to benefit from reduced costs and improved efficiency.
Overprovisioning and underprovisioning are costly, inefficient, and lead to improperly sized infrastructures. With overprovisioning, businesses end up with costly idle workloads. Overprovisioning commonly occurs during migrations to the cloud. Organizations use resource configuration calculations based on their on-premises workloads while failing to consider that virtual machines in the cloud are more efficient, resulting in overprovisioning. On the opposite end of the spectrum, organizations can easily underprovision resources, usually due to a desire to save early in the migration process. However, as workloads and demand increase, organizations end up with underperforming systems and major increases in latency.
One advantage of cloud computing is the ability to utilize auto-scaling and monitoring tools to help calculate resource requirements and right size infrastructure. While there is sometimes an increased cost for elastic services because of the gained flexibility, it is important to factor in as an option to a holistic cloud strategy – this comes down to specific workload composition and behavior.
Optimizing region selection
Cloud Regions and availability zones are important to cost optimization as different geographic areas offer advantages in performance and costs. Compute power and storage costs vary per region, therefore, choosing regions incorrectly can lead to unnecessary increased costs. Sometimes organizations simply lack visibility into where to place workloads. Since some regions have lower costs than others for the same resources, choosing regions carefully is part of a cost-conscious implementation strategy.
To add to the complexity of selecting a region, there are four factors that organizations must take into consideration:
- region compliance
- availability of services in a region
- cost of workloads in the region
- user location
Some workloads contain data bound by local regulations, so organizations need to ensure the regions they select are compliant and have the services they need. Region choice also has a significant impact on latency and user experience. The closer the region is to the user, the lower the latency and the better the performance. These factors need to be considered as an organization scales its cloud capability.
Addressing idle workloads
Idle workloads consist of any resources running and incurring costs while not being used. Identifying patterns of workload usage is vital to cost optimization in the cloud. Workloads will vary from project to project, so it’s important to utilize savings plans, when possible, for infrequently used resources. One common manifestation of this is when organizations leave instances running to provide high availability to their applications and fail to remove workloads as demand decreases, therefore leaving resources idle and accruing costs. This can be due to the difficulty of identifying patterns of workload usage and trying to scale resources manually. Simply not knowing how to properly identify unused resources or forgetting to delete them is another cost driver.
Cloud computing offers multiple solutions to handle idle workloads and mitigate costs. Automation and elastic features in the cloud, such as auto-scaling, allow organizations to benefit from resources automatically expanding and compressing as workload fluctuates. Cloud monitoring and scheduling tools can also help find these patterns and contribute to cost-saving opportunities. Lastly, a strong cloud governance strategy can help to create guardrails and processes to mitigate this issue.
Multi-cloud egress cost considerations
A multi-cloud strategy refers to using more than one cloud service provider to serve an organization. Data ingress refers to bringing data into the cloud and is usually free. Data egress refers to data being transferred out of the cloud and usually incurs cost. In a multi-cloud architecture, there can be egress fees when moving data across different providers. These can quickly add up and lead to surprisingly inflated costs.
These fees are not fixed and cannot be negotiated, so it is essential to have a strategy to manage costs. Egress costs can arise due to changing IT strategy, a new acquisition/merger, entering a new market, or relocating data due to regulations – to name a few sources.
They can be managed by optimizing network architecture, setting limits, avoiding duplication, and setting proper backup requirements. Another option is to set up private network connections, such as AWS Direct Connect and Azure ExpressRoute, which offer discounted egress fees.
The potential savings of Reserved Instances
Reserved Instances (RIs) allow organizations to reserve capacity for Amazon EC2 and RDS. By reserving a certain amount of capacity for one of these services, an organization can save up to 72% compared to on-demand pricing. RIs are extremely beneficial for predictable workloads that run consistently for a long period of time. However, organizations may choose to refrain from using RIs if they are working on short-term projects, have changing business needs, or are unwilling to make a one- or three-year commitment.
A reserved instance cannot be canceled, so customers are required to commit to one or three years to apply discounts. Additional discounts may be offered depending on the length of the commitment, the size of the instance, the region it is in, and the amount of the upfront payment made.
There are two types of reserved instances: standard and convertible. Standard Instances provide the highest level of savings (up to 72%), but these instances cannot be exchanged. They can only be modified to change the Availability Zone, the instance size, and networking type. Convertible Instances offer lower discounts (up to 66%) because they can be exchanged and modified. This option is better if additional flexibility is needed like the ability to use different instance families, operating systems, or tenancies during the RI term.
If your organization has predictable workloads and is not leveraging reserved instances, this would be a great area to explore with your cloud leaders.
Smart strategies for cloud cost optimization
As organizations tackle the challenges of the cloud, it is important to be aware of these hidden costs and optimize spending wherever possible. Better visibility into cloud environments helps with cost savings, performance, availability, and effective resource utilization. By embarking on the cloud cost optimization journey, organizations can avoid overspending, get more value for each dollar spent on the cloud, increase transparency of where money is being spent, and promote a cost-aware culture. By the end of the journey, organizations can build better habits to keep cloud costs optimized.
If your organization faces challenges across any of these areas, Pariveda has a bespoke offering to help tackle these costs and more. We would love to work with your organization to help implement long-term cost avoidance mechanisms and identify and execute short-term cost reductions.